Last Updated on February 13, 2024
There is a lot of misinformation about cooking oils and confusion about which oils are healthy or not.
Eating too much of the wrong kinds of oils can cause serious health issues.
And the wrong kinds are EVERYWHERE!
In this complete Healthy Cooking Oil Guide, I break down the best cooking oils, their fatty acid profile, smoke point, and flavor profiles, and TONS of tips to get the most flavor, nutrients, and health benefits.
Different oils have their own unique blend of fatty acids and health benefits. In addition to health benefits choosing the right oil depends on the type of cooking you intend to do.
An oil’s smoke point is the temperature at which it starts burning and producing smoke. It’s essential to avoid heating oil past its smoke point because doing so can negatively impact the flavor, nutrition content, and benefits. In fact, overheated oil can release harmful compounds known as free radicals. These free radicals can cause inflammation that’s linked to disease.
Some oils are healthy and others are not at room temperature.
But healthy oils can become harmful if they’re overheated, too.
It’s important to avoid cooking oil above its smoke point to ensure the best flavor and nutrition, and to avoid making oils unhealthy.
I’m going to do a breakdown of the best healthy cooking oils and what makes oil unhealthy so you know what to have in your kitchen.
So let’s dig into my complete guide to Healthy Cooking Oils including the best healthy oils for cooking, their fatty acid content, smoke points, flavor profile, and more.
What Oils Are Healthy?
Wondering what the heck makes an oil healthy or not? There are a few things to consider First, the type and ratio of fatty acids, then its smoke point.
Each fatty acid has its own characteristics and health benefits:
1. Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3s are considered essential fatty acids, meaning that our bodies cannot produce them and we need to obtain them from our diet. They play crucial roles in brain function, cardiovascular health, and inflammation regulation.
Omega-3s are commonly found in fatty fish (such as salmon and sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and certain oils like flaxseed oil and fish oil.
2. Omega-6 fatty acids: Similar to omega-3s, omega-6s are also essential fatty acids that our bodies require but cannot produce. Omega-6s are involved in the production of hormones and cell membranes. While necessary for overall health, excessive consumption of omega-6s relative to omega-3s can promote inflammation.
Common sources of omega-6s include vegetable oils (such as soybean oil, sunflower oil, and corn oil), nuts, seeds, and poultry. It’s best to avoid Omega 6 oils and eat nuts, seeds, and poultry with them to get the benefits you need and avoid health issues.
3. Omega-9 fatty acids: Omega-9s are non-essential fatty acids, meaning that our bodies can produce them on their own. They are commonly found in various oils like olive oil, avocado oil, as well as nuts and seeds.
Omega-9s are known for their potential benefits in supporting heart health and reducing inflammation.
Cooking oils are good sources of Omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9 fatty acids so it’s best to incorporate them into your diet.
What makes an oil healthy or unhealthy?
Omega 3, 6, & 9 omega fatty acids are all considered beneficial.
But health issues can occur when people have too many 6’s and not enough omega 3s. Excessive intake of omega-6 fatty acids, especially from processed and unhealthy sources, contributes to inflammation if not balanced with sufficient omega-3 intake. So if the oil is inflammatory it’s bad. And imbalanced fatty acids are also bad.
Balancing the intake of omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9 fatty acids is important for maintaining optimal health & avoiding issues.
The ideal ratio of omega-6 to omega-3 fatty acids in the diet is a topic of debate, but the holistic ratio recommended is 1:1. Others will say that 4:1 is ok, but I recommend the 1:1 ratio as fatty acids are a leading cause of death. Imbalances, left untreated can literally kill you.
A majority of people eating closer to a ratio of 15:1 – 20:1. A ratio this high is what set’s you up for disease.
It’s recommended to focus on whole food sources and a diverse diet to ensure a balanced intake of these fatty acids.
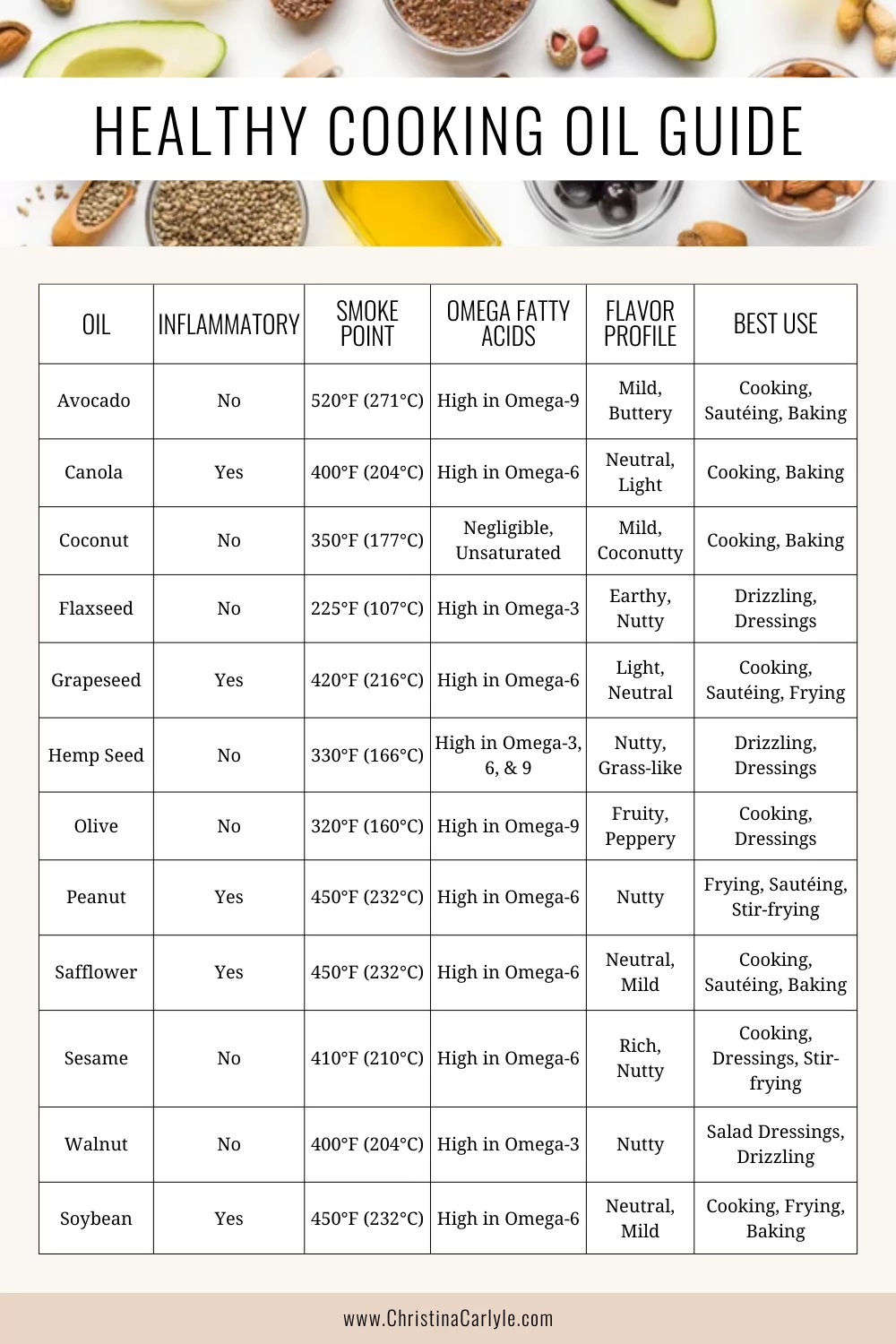
Healthy Cooking Oil Chart
*”Negligible” in reference to the omega-3 content of coconut oil and palm oil, I meant that they contain very minimal amounts of omega-3 fatty acids. These oils are primarily composed of saturated fats and do not significantly contribute to omega-3 intake in the diet.
Healthiest Oils for Cooking & Baking
The healthiest oils for cooking are typically those that are rich in monounsaturated fats and have a higher smoke point.
Here’s a backed-by-science list of the oils healthiest for cooking & baking:
Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is widely recognized as a healthy oil due to its high content of monounsaturated fats and beneficial compounds like polyphenols. It is suitable for low to medium-heat cooking methods.
Coconut Oil: Although coconut oil is high in saturated fats, it is unique in its composition and has medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) that may provide certain health benefits. It has a moderate smoke point and is suitable for baking and sautéing at lower temperatures.
Flaxseed Oil: Flaxseed oil is a good source of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). It has a low smoke point and is best used as a finishing oil or in recipes that don’t involve heat, such as salad dressings or drizzling over cooked dishes. I like this flaxseed oil.
Avocado Oil: Avocado oil is rich in monounsaturated fats and has a high smoke point, making it suitable for high-heat cooking such as frying, roasting, and grilling.
Sesame Oil: Sesame oil, particularly the toasted variety, adds a distinctive flavor to dishes and is commonly used in Asian cuisine. It has a medium smoke point and is best for stir-frying and low to medium-heat cooking.
COOKING OILS WITH THE MOST HEALTH BENEFITS
| Oil | Best Use Case | Additional Health and Healing Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| (Extra Virgin) Olive Oil | Cooking, Dressing | Rich in monounsaturated fats, polyphenols; may help reduce inflammation, support heart health, and improve blood sugar control. |
| Avocado Oil | Cooking, Grilling | High in monounsaturated fats; may help lower cholesterol, support eye health, and enhance nutrient absorption from foods. |
| Coconut Oil | Baking, Sauteing | Contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs); may provide quick energy, support brain health, and exhibit antimicrobial properties. |
| Flaxseed Oil | Finishing Oil | Rich in omega-3 fatty acids (ALA); may help reduce inflammation, support heart and brain health, and improve skin and hair condition. |
| Walnut Oil | Dressing, Dipping | High in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and polyphenols; may support heart health, brain function, and have anti-inflammatory properties. |
Extra Virgin Olive Oil
When it comes to the healthiest oil to cook with, extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) takes the lead. It is widely recognized for its numerous health benefits. Here’s why I consider it my go-to choice:
EVOO is packed with health-promoting properties, including:
- Monounsaturated fats help lower LDL cholesterol levels
- Antioxidants that combat oxidative stress
- Anti-inflammatory compounds like oleic acid
- An abundance of polyphenols, which are micronutrients with various health benefits
- it’s easy to find
- is affordable compared to other healthy cooking oils
- has a great flavor and can be used in most cooking methods
Olive oil contains little omega-3, a little omega-6, but above all a lot of omega-9! This monounsaturated fatty acid is also a “good fat”. It is excellent for maintaining heart health and reducing hypercholesterolemia. Another reason why Olive oil is so popular is that it has exceptional antioxidant properties that help reduce oxidative stress in the body and thus prevent many diseases.
Olive oil is a key component of the Mediterranean diet, often associated with longevity, healing, and weight loss. People living in Blue Zones, where individuals tend to live longer, frequently use extra virgin olive oil in their cooking. It might just be their secret to a long and healthy life!
When it is of good quality, olive oil is a precious ally… and extra virgin is the best.
What’s the difference between olive oil and extra virgin olive oil?
Regular olive oil is a blend of pressed and processed olive oil, while extra virgin olive oil is obtained through a cold-pressing process and undergoes natural filtration to remove impurities. The purity and quality of extra virgin olive oil make it my top recommendation for healthy cooking.
But is it healthy to cook with extra virgin olive oil? Absolutely! Contrary to some beliefs, EVOO is perfectly suitable for cooking at medium to medium-high heat, such as sautéing and roasting vegetables. It has a smoke point ranging between 325-400ºF (163-204ºC), depending on the quality. When roasting vegetables, the oil on the surface aids in the roasting process without reaching the oven’s ambient temperature. However, it’s important to note that EVOO is not ideal for deep-frying.
How to get the best quality Extra Virgin Olive Oil?
When purchasing extra virgin olive oil, beware of counterfeit products. Many bottles contain additives and other undisclosed oils. To ensure you’re getting 100% real extra virgin olive oil, look for the following:
- Slight bitterness and a fresh aroma
- Avoid terms like “pure” or “light” on the label
- Choose brands you trust – Verify that the label explicitly states “100% extra virgin olive oil” and be cautious with cheaper brands, as they might be blended with lower-quality oils
- Opt for unrefined extra virgin olive oil, as “light” olive oil is refined and less heart-healthy than EVOO
- Get your extra virgin olive oil in glass – Plastic packaging can leach into your oil and then into you!
By selecting authentic and high-quality extra virgin olive oil, you soak in the health benefits and enhance your culinary creations.
COCONUT OIL
Coconut oil is widely used in cooking and food products, it has a different nutritional profile compared to other vegetable and seed oils. Coconut oil is higher in saturated fats and lower in unsaturated fats. Some coconut oil critics will say that coconut oil is too high in saturated fats and should be avoided but that’s simply not the case.
Here’s a list of good reasons to use coconut oil in your diet.
Cooking Benefits:
- High Smoke Point: Coconut oil has a high smoke point, making it suitable for various cooking methods like frying, sautéing, and baking at moderate temperatures.
- Flavor Enhancer: It imparts a distinct tropical flavor to dishes, adding a delightful taste to both sweet and savory recipes.
- Versatile Ingredient: Coconut oil can be used in a wide range of recipes, from stir-fries and curries to baked goods and smoothies.
Health Benefits:
- Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCTs): Coconut oil contains a high concentration of MCTs, which are easily digestible fats that are quickly converted into energy by the body.
- Potential Boost in Good Cholesterol: Studies suggest that the consumption of coconut oil may raise levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, commonly known as “good” cholesterol.
- Promotes Satiety: MCTs in coconut oil have been linked to increased feelings of fullness and reduced calorie intake, potentially aiding in weight management.
- Skin and Hair Care: When applied topically, coconut oil can moisturize the skin, promote hair health, and provide a protective barrier against damage. Try this foot scrub for healthy, smooth feet.
Antimicrobial Applications:
- Lauric Acid Content: Coconut oil contains lauric acid, which has antimicrobial properties and may help combat certain bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Oil Pulling: You can literally swish coconut oil in your mouth (oil pulling) to boost your mouth health. Oil pulling is an ancient practice used to reduce harmful bacteria and improve gum health. It’s recommended if you have any oral or gut health issues.
It’s important to note that while coconut oil has its benefits, it is high in saturated fat, so moderation is key and using coconut oil along with olive oil will prevent issues.
Using extra virgin olive oil along with coconut oil is a great combination to have in your kitchen… but there’s one more healthy cooking oil I would recommend having in your collection.
Flaxseed Oil
Flaxseed oil would tie for #3 on my healthy cooking oil list… and for good reason. Flaxseed oils contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential.
Flaxseed oil, derived from flaxseeds, offers several potential health benefits due to its nutritional profile. Here are some benefits associated with consuming flaxseed oil:
- Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Flaxseed oil is a concentrated source of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an essential omega-3 fatty acid. Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in supporting heart health, brain function, reducing inflammation, and promoting overall well-being.
- Cardiovascular Support: The omega-3 fatty acids found in flaxseed oil may help lower the risk of heart disease by reducing inflammation, improving blood vessel function, and helping to maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
- Brain Health: Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are essential for brain development and function. Flaxseed oil can contribute to maintaining optimal brain health and may have potential benefits for cognitive function.
- Joint Health: The anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3 fatty acids in flaxseed oil may help alleviate joint pain and stiffness associated with conditions like arthritis. It may also contribute to maintaining joint flexibility and reducing inflammation in the body.
- Skin Health: Flaxseed oil contains essential fatty acids that can help nourish and hydrate the skin from within. Regular consumption may improve skin texture, promote a healthy complexion, and reduce dryness or irritation.
- Hormonal Balance: Flaxseed oil contains lignans, which are natural plant compounds that can have estrogen-like effects in the body. These lignans may help balance hormone levels, particularly in women experiencing hormonal imbalances or menopausal symptoms.
- Digestive Health: Flaxseed oil’s lubricating and soothing properties may benefit the digestive system. It can help promote regular bowel movements, alleviate constipation, and support overall gut health.
- Potential Anti-Cancer Properties: Some studies suggest that flaxseed oil’s lignans may have anti-cancer properties and may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including breast, prostate, and colon cancer. However, further research is needed to establish conclusive evidence.
Again cutting them with canola or other filler oils is a common practice so make sure your flaxseed oils is 100% flaxseed oil and from a reputable brand.
If you can’t find a healthy flaxseed oil you can also eat flaxseeds to reap the benefits. Flaxseeds are great when blended into smoothies, tossed onto salads and sides, and toasted as a snack.
Infuse Cooking Oils for more Health Benefits & Flavor
Adding flavor to oils is a great way to enhance your dishes and create unique culinary experiences. Here are some methods for infusing oils with delicious flavors:
- Herbs and Spices: Add fresh or dried herbs and spices to your oil and let them steep for a period of time. Popular choices include rosemary, thyme, basil, garlic, chili flakes, or peppercorns. You can experiment with different combinations to achieve the desired flavor profile.
- Citrus Zest: Citrus fruits like lemons, limes, oranges, or grapefruits can add a refreshing and vibrant flavor to oils. Use a peeler or zester to remove the colored part of the citrus peel (avoid the bitter white pith) and place it in the oil. Allow it to infuse for a while before using.
- Roasted Ingredients: Roasting certain ingredients can release their natural oils and flavors. For example, roasted garlic or roasted chili peppers can be combined with oil to create a rich and aromatic infusion.
- Nuts and Seeds: Toasted nuts and seeds can provide a nutty and flavorful twist to oils. Crush or grind the nuts or seeds and mix them with the oil. Popular choices include toasted sesame seeds, almonds, or pine nuts.
- Balsamic Vinegar: Combine your cooking oils with balsamic vinegar for a jolt of tangy flavor
- Dried Mushrooms or Truffles: Dried mushrooms, such as porcini or shiitake, can add an earthy and umami flavor to oils. You can also use truffle oil or fresh truffle shavings to infuse the oil with a luxurious and distinctive taste.
To infuse the flavors, simply combine the desired ingredients with the oil and let them sit for a period of time, allowing the flavors to meld. The length of time will depend on the intensity of the ingredients and your personal preference. Once infused, strain the oil to remove any solid particles before using or storing it.
Best Healthy Cooking Methods for Oils
When cooking with oils, there are certain methods that can help preserve the nutritional value of the food and minimize the negative effects of excessive heat. Here are some of the best and healthiest cooking methods when using oils:
- Sautéing and Stir-Frying: These methods involve quickly cooking food in a small amount of oil over medium to high heat. It allows for fast cooking while retaining the natural flavors and nutrients of the ingredients.
- Baking and Roasting: These methods involve cooking food in the oven using indirect heat. It requires minimal oil and helps to enhance the natural flavors of the ingredients without excessive oil absorption.
- Steaming: Steaming involves cooking food using the steam generated from boiling water. It is a gentle cooking method that doesn’t require the use of oil. It helps to retain the nutrients, texture, and flavors of the food.
- Grilling: Grilling involves cooking food on a grill or barbecue. It allows excess fat to drip off, resulting in a lower oil content. Grilling can add a unique smoky flavor to the food without the need for excessive oil.
- Poaching: Poaching involves cooking food in a simmering liquid such as water, broth, or milk. It is a low-fat cooking method that helps retain the moisture and delicate flavors of the food.
- Steaming in Parchment Paper or Foil: This method involves wrapping food in parchment paper or foil and cooking it in the oven. It helps seal in moisture and flavors without the need for excessive oil.
It’s important to note that the type and amount of oil used in these cooking methods should be considered. Opt for healthier oils with a higher smoke point, such as olive oil, avocado oil, or coconut oil, as they are more stable at higher temperatures.
Also, moderation is key – using excessive amounts of oil in any cooking method can contribute to increased calorie intake.
Health Issues Associated with Unhealthy Oils
Consuming excessive amounts of omega-6 fatty acids relative to omega-3 fatty acids can potentially lead to several health issues.
Here are some possible consequences of an imbalanced ratio or excessive intake of omega-6 fatty acids:
- Inflammation: Omega-6 fatty acids, when consumed in excess, can promote inflammation in the body. While inflammation is a normal response to injury or infection, chronic inflammation has been associated with various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, and certain types of cancer.
- Imbalanced Omega-3 to Omega-6 Ratio: Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids have opposing effects in the body. An excessively high intake of omega-6 fatty acids can disrupt the ideal balance between omega-3 and omega-6, which is typically recommended to be around a 1:1 to 1:4 ratio. This imbalance may hinder the beneficial effects of omega-3 fatty acids and contribute to health issues related to inflammation and cardiovascular health.
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Studies suggest that an imbalance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, with excessive omega-6 intake, may increase the risk of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and certain inflammatory conditions.
- Adverse Cardiovascular Effects: Consuming an excess of omega-6 fatty acids, particularly when coupled with a low intake of omega-3 fatty acids, may lead to unfavorable changes in blood lipid profiles, such as increased levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and decreased levels of HDL (good) cholesterol. These changes can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Immune System Dysregulation: Omega-6 fatty acids play a role in immune responses, but excessive intake can disrupt the proper functioning of the immune system and contribute to immune-related disorders.
It’s important to note that omega-6 fatty acids are still essential for the body and have beneficial effects when consumed in moderation and as part of a balanced diet.
The key is to maintain a healthy balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids by incorporating oils and foods rich in omega-3s, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, while being mindful of the sources and amounts of omega-6 fatty acids consumed.
It’s also important to prevent healthy oils from becoming unhealthy and avoid the inflammatory sources of cooking oils.
What makes cooking oils unhealthy?
Remember, even a healthy oil can become unhealthy if it’s heated beyond its smoke point.
HEATING OILS MAKE THEM INFLAMMATORY
Heating oils beyond their smoke point can lead to the production of harmful compounds, which may contribute to inflammation in the body. When oils are exposed to high heat, they undergo chemical changes that can generate potentially inflammatory substances.
During the heating process, several reactions occur in the oil. One of the most significant changes is the breakdown of the oil’s fatty acids into smaller molecules called free fatty acids. These free fatty acids can undergo oxidation, resulting in the formation of harmful compounds such as lipid peroxides, aldehydes, and advanced glycation end products (AGEs).
These compounds have been associated with oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of harmful free radicals and the body’s ability to neutralize them. Inflammatory processes can be triggered by the presence of these free radicals and the resulting cellular damage.
Additionally, when oils are heated, their molecular structure may change, leading to the formation of trans fats and other harmful byproducts. Trans fats have been well-documented to have inflammatory effects and are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and other health problems. You should NEVER eat trans fats.
It’s important to note that not all oils have the same smoke point, and some oils are more stable at high temperatures than others. Choosing oils with higher smoke points and using appropriate cooking methods, such as sautéing or stir-frying instead of deep-frying, can help minimize the formation of harmful compounds.
To reduce the potential inflammatory effects of heated oils, it’s advisable to use oils with higher smoke points for high-heat cooking and to avoid reusing oils that have been heated multiple times. Incorporating a variety of healthy oils into your diet, including those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and balancing omega-6 and omega-3 intake can also contribute to a more favorable inflammatory response in the body.
DILUTING HEALTHY OILS
It is not a common practice for reputable food manufacturers to dilute olive oil with inflammatory oils intentionally. However, it’s essential to be aware that fraud and adulteration can occur in the food industry, including the olive oil market.
There have been cases where lower-quality oils or other vegetable oils have been mixed with or sold as olive oil. This is typically done to reduce costs and increase profits. These adulterated oils may include oils with higher levels of omega-6 fatty acids, which, when consumed in excess, can contribute to inflammation.
To ensure you are purchasing high-quality olive oil, it’s advisable to choose reputable brands, look for certifications of authenticity, and consider purchasing from sources that provide transparency about their production processes. Extra virgin olive oil is generally considered the highest quality and least processed form of olive oil, so selecting that variety can also help minimize the risk of adulteration.
So when looking for a healthy oil make sure the oil itself is the only ingredient listed.
Common Food Sources of Unhealthy Oils
- Vegetable Oils: Oils derived from soybeans, corn, safflower, sunflower, and cottonseed are commonly used in processed foods and cooking. These oils tend to be higher in omega-6 fatty acids.
- Processed and Fried Foods: Many processed and fried foods, such as fast food, pre-packaged snacks, chips, and deep-fried items, are often cooked using oils rich in omega-6 fatty acids.
- Salad Dressings and Mayonnaise: Store-bought salad dressings and commercial mayonnaise often contain vegetable oils, which are commonly high in omega-6 fatty acids.
- Margarine and Shortening: These butter substitutes are often made from partially hydrogenated oils, which can be high in omega-6 fatty acids.
- Baked Goods: Commercially prepared baked goods like cookies, pastries, cakes, and muffins often contain vegetable oils or shortenings high in omega-6 fatty acids.
- Snack Foods: Many snack foods, including crackers, granola bars, and popcorn, may be made with oils high in omega-6 fatty acids.
- Rotisserie Chicken: Rotisserie chicken itself is not a significant source of omega-6 fatty acids. Store-bought, commercially prepared rotisserie chickens are commonly basted with soybean or vegetable oils to season the chickens and make them crispy. These oils contribute to omega-6 intake. Opt for organic chickens and ask your grocer about your options to avoid omega 6’s
So there you have it!
The complete guide to Healthy Cooking Oils.
I hope this post helped you!!
If it did, let me know in the comments.
Don’t forget to sign up as a VIP so you don’t miss my next free training.
xo
Your Coach & Biggest Cheerleader,
![]()
Pin this post to Pinterest so you’ll have it forever.
If you liked this article you’ll love everything else in my Best Foods for Weight Loss (and Health) Series:
- Best Protein Powders for Weight Loss
- Best Supplements for Weight Loss
- Best Fruits for Weight Loss
- Best Vegetables for Weight Loss
- Best Nuts for Weight Loss
- Best Milk for Weight Loss
- Best Carbs for Weight Loss













Thank You so much for this post!
I have been trying to figure out the best healthy oils to cook with. Growing up, my mama always used vegetable oil and that is what i have been using in cooking for my family. I have recently found out that that oil is not healthy.
This post was just what I needed. Thanks again!!!
Awesome! I’m so happy you found the guide helpful. xo