Last Updated on June 17, 2023
You’ve heard of probiotics but what about prebiotics?
Prebiotics are mandatory if you want to experience the benefits of probiotics, stay healthy, and optimize your metabolism.
I find that most of my clients don’t know much about them.
Do you know what prebiotics are and what they do?
Do you know the different types of prebiotics, their benefits, and the best sources of them?
HINT: Unlike probiotics the best sources of prebiotics are foods… NOT supplements.
If you don’t know how to answer these questions, don’t worry!
By the end of this post, you’ll be a prebiotic pro!
I’m going all in to teach you about prebiotics so this is a must-read.
And yes, there are benefits to prebiotics so buckle up, buttercup.
Here you’ll learn:
- What prebiotics are and what they do
- How prebiotics affect weight loss
- Prebiotic Benefits
- Symptoms & signs you need (more) prebiotics
- The different types of prebiotic fibers
- Foods highest in prebiotics
- Intake Guidelines for the best results
What are Prebiotics and What Do They Do?
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that act as a food source for beneficial bacteria in the gut. They are not broken down or absorbed in the upper digestive tract but instead reach the colon intact, where they selectively stimulate the growth and activity of specific beneficial bacteria.
Prebiotics play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy balance of the gut microbiota and supporting optimal gut health, immunity, and metabolism.
By nourishing beneficial bacteria, prebiotics can help improve digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, strengthen immune function, and boost potential benefits for weight management.
How Prebiotics Affect Weight Loss
Prebiotics can play a role in weight loss through several mechanisms:
- Increased satiety: Prebiotics, particularly soluble fibers like inulin and oligofructose, have the ability to increase feelings of fullness and satiety. By promoting a sense of satisfaction after meals, prebiotics can help reduce overall calorie intake, which can support weight loss efforts.
- Improved nutrient absorption: Prebiotics contribute to a healthier gut environment by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. These beneficial bacteria play a role in enhancing nutrient absorption, particularly the absorption of dietary fats. By improving nutrient uptake, prebiotics can help optimize the body’s metabolism and potentially support weight loss.
- Regulation of blood sugar levels: Certain prebiotics, such as resistant starch and soluble fibers, can help regulate blood sugar levels. By slowing down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, prebiotics can prevent spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels. This can promote more stable energy levels and reduce cravings for sugary or high-calorie foods, aiding in weight management.
- Reduced inflammation: Imbalances in the gut microbiome and chronic inflammation have been linked to weight gain and obesity. Prebiotics have shown potential in reducing inflammation and promoting a healthier gut environment. By supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria and suppressing the growth of harmful microbes, prebiotics can help reduce systemic inflammation, which may indirectly contribute to weight loss.
Benefits
Prebiotics offer several health benefits, including:
- Gut Health: Prebiotics promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, helping to maintain a healthy balance of the gut microbiota. This can contribute to improved digestion, reduced risk of gastrointestinal disorders, and enhanced overall gut health.
- Enhanced Nutrient Absorption: By supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria, prebiotics can enhance the absorption of certain minerals, such as calcium and magnesium, in the gut. They may also improve the utilization of other nutrients, such as vitamins and antioxidants.
- Strengthened Immune System: A healthy gut microbiota, fostered by prebiotics, plays a crucial role in supporting a strong immune system. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, prebiotics help to regulate immune responses, reduce inflammation, and enhance the body’s ability to fight off pathogens.
- Improved Bowel Regularity: Prebiotics can contribute to regular bowel movements and help alleviate constipation by increasing the bulk and softness of stools. They provide nourishment for bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids, which support healthy bowel function.
- Weight Management: Some research suggests that prebiotics may play a role in weight management. They can increase feelings of fullness, regulate appetite, and potentially influence energy metabolism, which may help with weight loss or maintenance.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: A healthy gut microbiota influenced by prebiotics is associated with a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain gastrointestinal disorders.
If you have any of the following symptoms I’d recommend prioritizing your prebiotic intake in addition to following my Total Transformation Program.
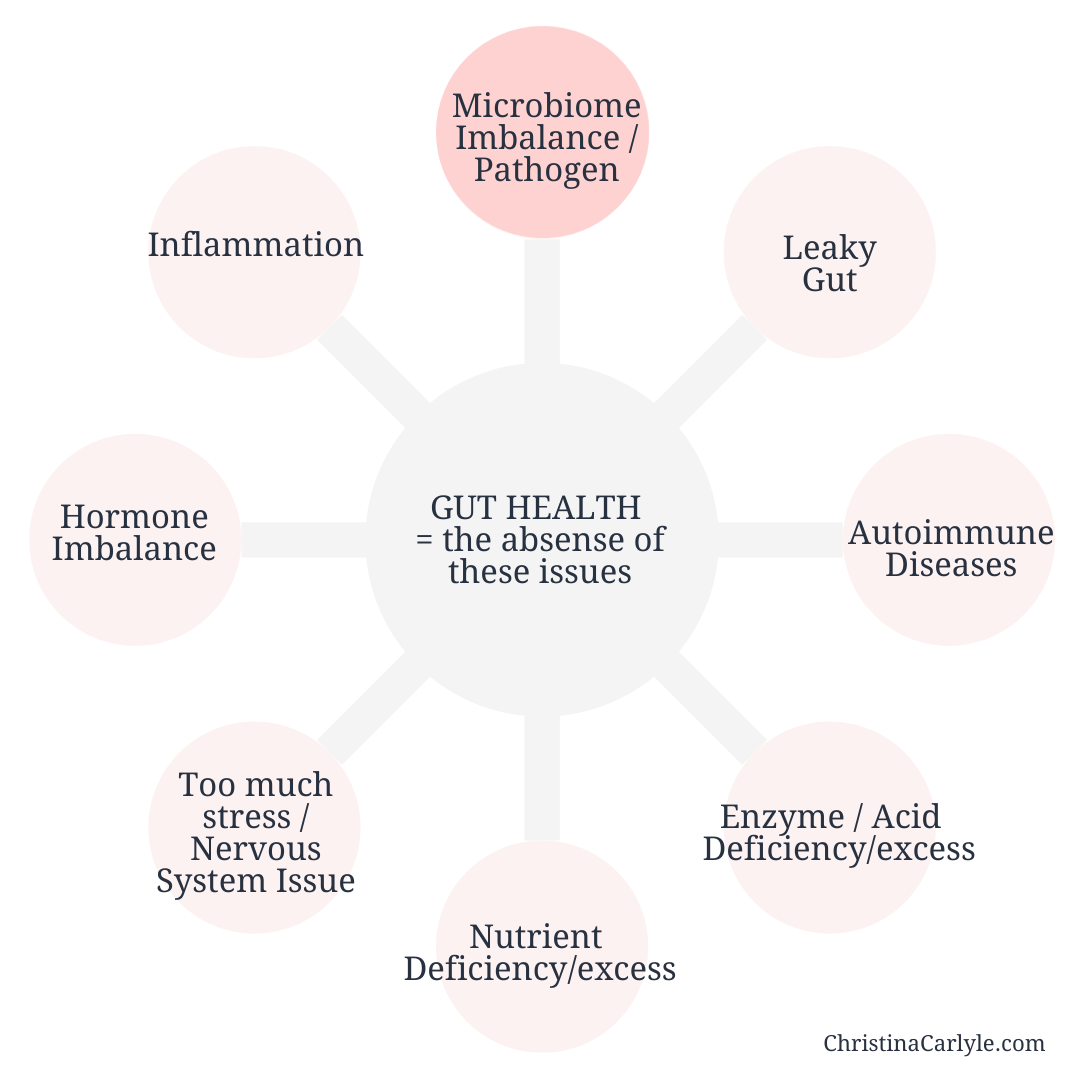
Symptoms & Signs you need more prebiotics
The following gut health symptoms indicate that you’d benefit from adding more prebiotics (and probiotics) into your diet.
Do you have any of these GI symptoms?
It’s important to note that the specific benefits vary depending on the type and amount of prebiotics consumed, individual factors, and overall dietary and lifestyle habits.
Including a variety of prebiotic-rich foods in your diet can contribute to these potential health advantages and support overall well-being.
It’s critical to consume pre-biotics as a part of a complete meal plan while avoiding things like inflammation, hormone imbalances, stress, leaky gut, an overburdened liver, etc.
If you’re serious about healing your gut and losing weight use my Total Transformation Program.
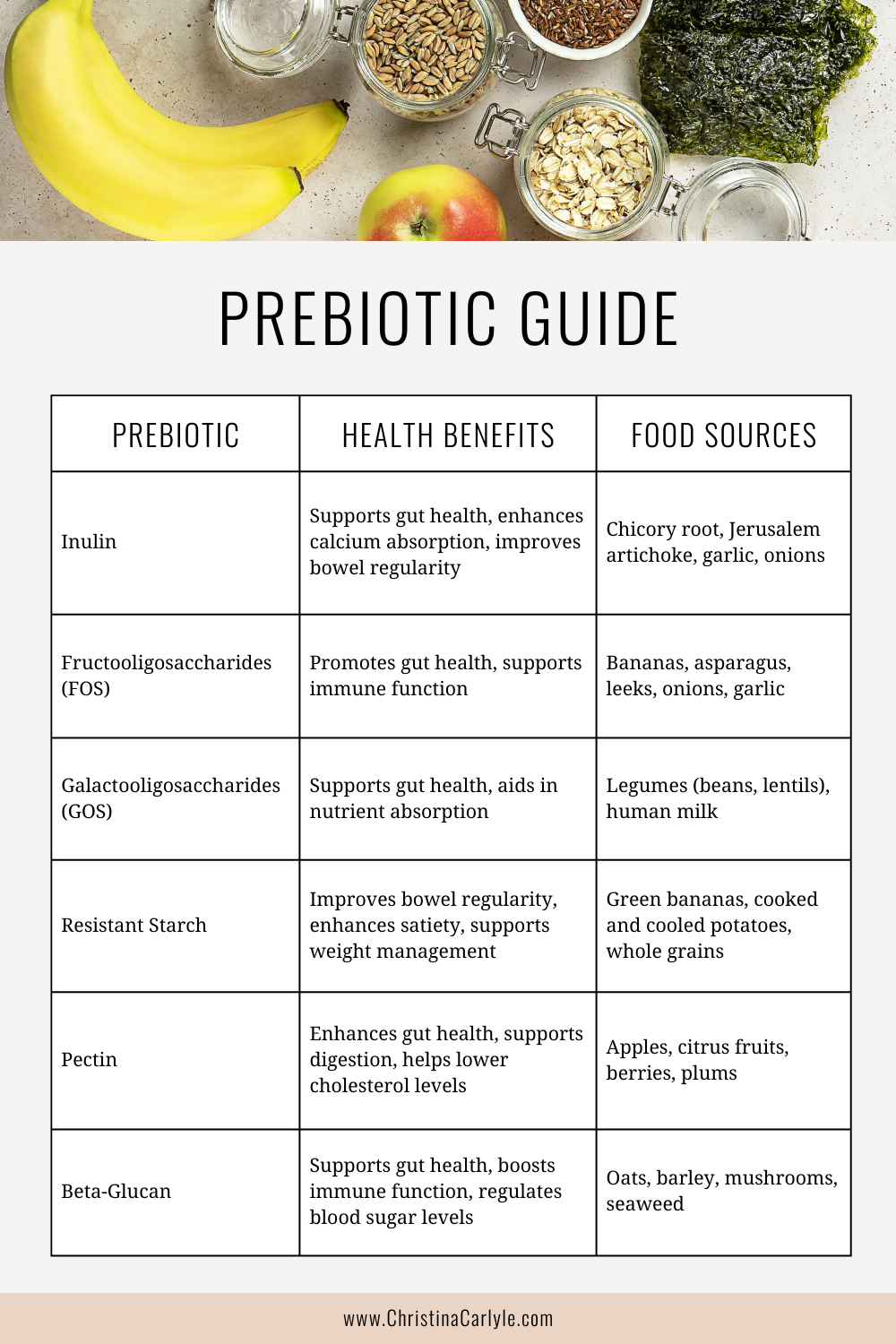
DIFFERENT TYPES OF PREBIOTIC FIBERS
Prebiotics include inulin, fructooligosaccharides (FOS), galactooligosaccharides (GOS), resistant starch, and various types of dietary fibers found in certain fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
- Inulin: Inulin is a type of soluble fiber found in many plants, such as chicory root, Jerusalem artichoke, and asparagus. It is widely used as a prebiotic supplement due to its ability to stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria, particularly Bifidobacteria.
- Fructooligosaccharides (FOS): FOS are a group of short-chain carbohydrates found in foods like bananas, onions, garlic, and leeks. They act as prebiotics by selectively promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Galactooligosaccharides (GOS): GOS are another group of prebiotic carbohydrates that can be found in human breast milk and certain legumes, such as lentils and chickpeas. They are not digested by the human body but are utilized by beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Resistant Starch: Resistant starch is a type of starch that resists digestion in the small intestine and reaches the colon intact. It can be found in foods like green bananas, raw oats, and cooked and cooled potatoes. Resistant starch acts as a prebiotic by providing nourishment to beneficial bacteria.
- Lactulose: Lactulose is a synthetic prebiotic made from lactose. It is not well digested by humans but can be fermented by beneficial bacteria in the colon, promoting their growth.
- Pectins & Gums: Certain gums and pectins, such as guar gum, acacia gum, and citrus pectin, have prebiotic properties. They are commonly used as food additives and can help support the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Beta-Glucan: Beta-glucan is a type of soluble fiber found in oats, barley, mushrooms, and certain seaweeds. It has been shown to have prebiotic effects by selectively stimulating the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, such as Bifidobacteria.
- Pectin: Pectin is a type of soluble fiber found in fruits, particularly in the peels and pulp of apples, citrus fruits, and berries. It acts as a prebiotic by providing nourishment to beneficial bacteria in the gut and promoting their growth.
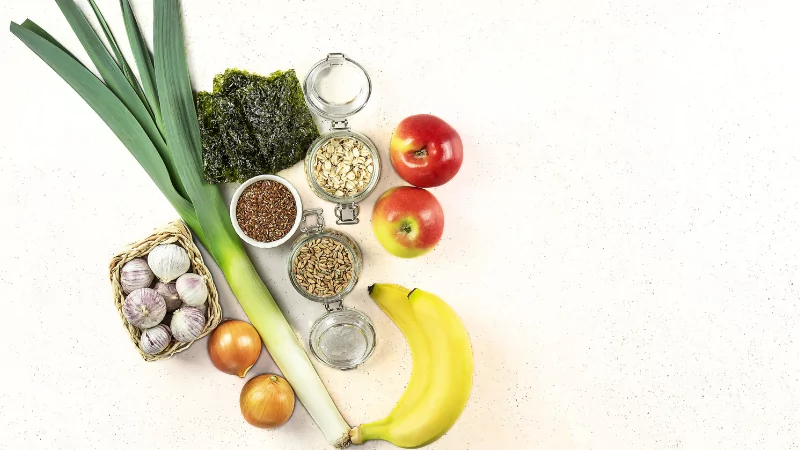
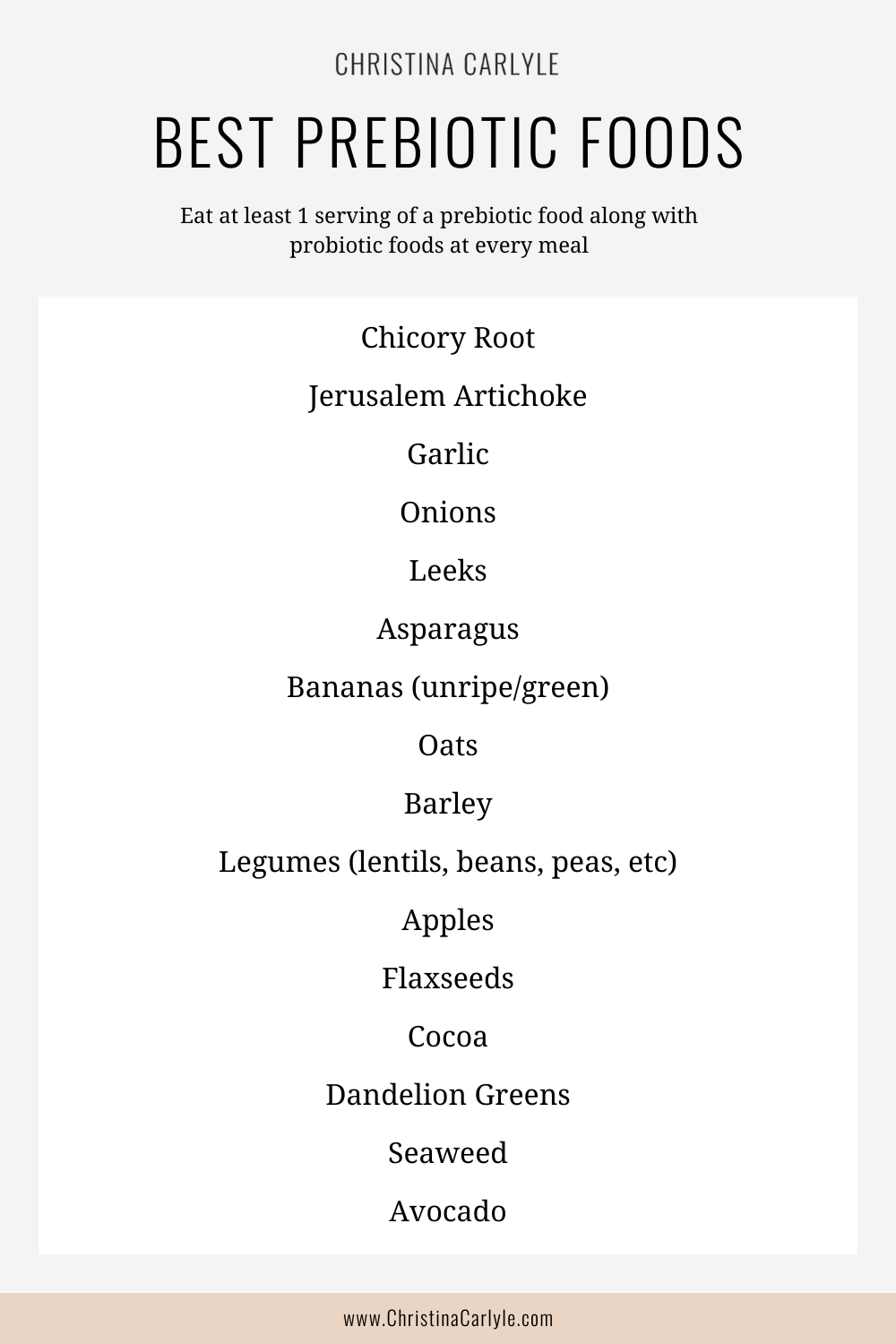
FOODS HIGHEST IN PREBIOTICS
- Chicory Root: This root vegetable is one of the richest sources of prebiotic fibers, particularly inulin.
- Jerusalem Artichoke: Also known as sunchokes, these tuberous vegetables are high in inulin and make a great addition to various dishes.
- Garlic: This flavorful bulb contains prebiotic fibers like inulin and FOS (fructooligosaccharides).
- Onions: Both raw and cooked onions are rich in prebiotic fibers, including inulin and FOS.
- Leeks: Similar to onions and garlic, leeks contain prebiotic fibers that can support a healthy gut.
- Asparagus: This versatile vegetable contains prebiotic fibers, including inulin, which can nourish beneficial gut bacteria.
- Bananas: While ripe bananas have a lower prebiotic content, unripe or green bananas are high in resistant starch, which acts as a prebiotic.
- Oats: Oats are a good source of prebiotic fibers, such as beta-glucan, which can support gut health.
- Barley: This whole grain contains prebiotic fibers, including beta-glucans, and can be used in soups, stews, and salads.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, beans, and peas are legumes that provide prebiotic fibers like GOS (galactooligosaccharides).
- Apples: Apples contain pectin, a type of fiber that can act as a prebiotic and support gut health.
- Flaxseeds: These tiny seeds are a good source of prebiotic fibers, including mucilage, which can help feed beneficial gut bacteria.
- Cocoa: Cocoa powder and dark chocolate contain prebiotic fibers, such as inulin, that can have a positive impact on gut health.
- Dandelion Greens: These bitter greens are rich in prebiotic fibers, including inulin, which can help support a healthy gut microbiome.
- Seaweed: Certain types of seaweed, such as kelp and kombu, contain prebiotic fibers that can promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Avocado: Avocado is a nutritious fruit that contains prebiotic fiber, contributing to a healthy gut microbiota.
Intake Guidelines FOR WEIGHT LOSS & Wellness
Eating both prebiotics (& probiotics) help stop cravings, regulate hunger, and blood sugar. They also help repopulate the gut microbiome which improves mood, immunity, metabolism, and energy.
It’s important to consume a diet rich in organisms and fiber… doing so creates an environment in which healthy probiotics can thrive.
To lose weight you have to feed the microbes that encourage weight loss. Without a high pro & prebiotic diet it’ll be difficult to maintain healthy pre & probiotic levels needed to see/feel results.
These following pro and prebiotic foods help reduce visceral fat, which is particularly harmful and associated with chronic diseases.
I recommend eating at least one serving of pro and prebiotics at every meal.
| Probiotic Foods | Prebiotic Foods |
|---|---|
| Yogurt | Chicory Root |
| Kefir | Jerusalem Artichoke |
| Sauerkraut | Garlic |
| Kimchi | Onions |
| Kombucha | Leeks |
| Miso | Asparagus |
| Tempeh | Bananas (unripe/green) |
| Pickles | Oats |
| Fermented Soy Products (e.g., Natto) | Barley |
| Buttermilk | Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, beans, peas) |
| Probiotics | Apples |
| Flaxseeds | |
| Cocoa | |
| Dandelion Greens | |
| Seaweed | |
| Avocado |
HOW TO USE PREBIOTICS (AND PROBIOTICS) TO LOSE WEIGHT
Adding (a lot) more probiotics and prebiotics into your diet can help prevent and reverse symptoms and help you lose weight… assuming you’re also NOT consuming things that fuel bad pathogenic gut microbes.
Here’s a simple protocol to use probiotics help boost gut health, reverse symptoms, maximize metabolism, and lose weight:
- Cut out bad-gut foods, drinks, supplements, and consumables & eat a diet that promotes gut health and healing. You can’t heal the gut simply by eating healthy… you have to avoid the wrong things and eat the right things to heal the gut and reverse inflammation, microbiome, hormone, toxicity, metabolic, and nutrient absorption issues. (That’s what my Total Transformation Program does)
- Repopulate your gut with a quality probiotic. See the shelf-stable Probiotics (and digestive health) supplements I recommend
- Eat high Probiotic and Prebiotic foods with every meal. (at least one serving of both per meal.)
- Eat gut healing foods.
- Engage in a healthy lifestyle & other healthy habits that support gut health and metabolism (like stress management, hydration, exercise, supplementation, etc. – all of which are covered in my Total Transformation Program)
- Radically reduce stressors in your life and use healthy coping skills.
\When you combine the right diet + healing protocols & supplements you’ll get results you can see and feel a LOT faster.
You have to have all steps in place to get benefits… if you’ve taken a probiotic before but didn’t feel a difference it’s because you were missing the other two critical steps!
\When you combine the right diet + healing protocols & supplements you’ll get results you can see and feel a LOT faster.
You can’t really fix a problem if your diet is causing issues in the first place. And prebiotic foods and probiotic supplements won’t do much if you’re fueling inflammation and pathogens with a bad diet.
If you really want to clean up your diet, heal your gut, reverse inflammation, balance hormones, and get rid of fatigue and cravings – AND lose weight – you need my Total Transformation Program.
Use my mini protocol + Gut Health and Weight Loss Guide + the pre and probiotics that I recommend along with my Total Transformation Program for the best results.
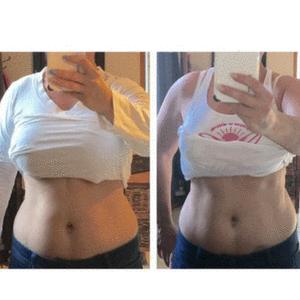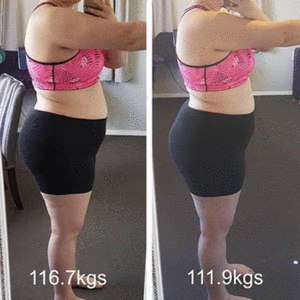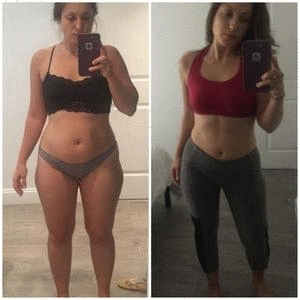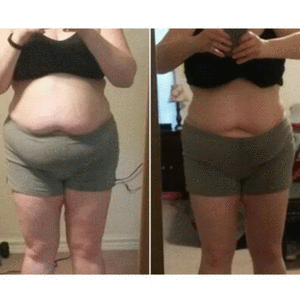
4 week before and afters on my Total Transformation Program
I hope this helped you understand the link between probiotics and weight!
Leave me a comment and let me know if you’re eating enough in your daily diet. If you’re not I hope this inspired you to start…
Because a happy, healthy gut is key to balancing hormones, reversing inflammation, burning fat, getting fit, and feeling awesome.
Remember if you want to burn fat, feel great and get fit fast, my Total Transformation Program can make it happen in 4 weeks flat.
xo
Your Coach and Biggest Cheerleader,
![]()
MORE GUT HEALTH & WEIGHT LOSS INFO
Check out these related articles to fill in more of the “gut health puzzle” so you’ll understand more about the different aspects of gut health, how they cause symptoms & weight gain, and how to optimize your gut health to maximize your weight loss potential:
- Gut Health and Weight Loss
- What are Probiotics?
- Probiotics and Weight Loss
- What are Prebiotics?
- The Best Foods for Gut Health
- What is Leaky Gut?
- Gut Health Supplements
- Intestinal Inflammation
- Gut Microbiome
Remember, if you have gut health symptoms you most likely also have metabolic dysfunction. This free training explains more about metabolic dysfunction & how I fix it so you can lose weight & feel great ASAP.